lagrange: Method of Lagrange Multipliers
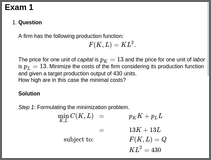
lagrangeA firm has the following production function: \[ F(K,L)= K L^{2}. \] The price for one unit of capital is \(p_K = 13\) and the price for one unit of labor is \(p_L = 13\). Minimize the costs of the firm considering its production function and given a target production output of 430 units.
How high are in this case the minimal costs?
Step 1: Formulating the minimization problem. \[ \begin{aligned} \min_{K,L} C(K,L) & = p_K K + p_L L\\ & = 13 K + 13 L\\ \mbox{subject~to:} & F(K,L) = Q \\ & K L^{2} = 430 \end{aligned} \] Step 2: Lagrange function. \[ \begin{aligned} \mathcal{L}(K, L, \lambda) & = C(K, L) - \lambda (F(K, L) - Q) \\ & = 13 K + 13 L - \lambda (K L^{2} -430) \end{aligned} \] Step 3: First order conditions. \[ \begin{aligned} \frac{\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial K} & = 13 - \lambda L^{2} = 0\\ \frac{\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial L} & = 13 - {2} \lambda K L^{2 - 1} = 0 \\ \frac{\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial \lambda} & = -(K L^{2}-430) = 0 \end{aligned} \] Step 4: Solve the system of equations for \(K\), \(L\), and \(\lambda\).
Solving the first two equations for \(\lambda\) and equating them gives: \[ \begin{aligned} \frac{13}{L^{2}} & = \frac{13}{2 K L^{2 - 1}}\\ K & = \frac{13}{2 \cdot 13} \cdot L^{2 - (2 - 1)}\\ K & = \frac{13}{26} \cdot L \end{aligned} \] Substituting this in the optimization constraint gives: \[ \begin{aligned} K L^{2} & = 430\\ \left(\frac{13}{26}\cdot L \right) L^{2} & = 430\\ \frac{13}{26} L^{3} & = 430\\ L & = \left(\frac{26}{13} \cdot 430\right)^{\frac{1}{3}} = 9.5096854 \approx 9.51\\ K & = \frac{13}{26} \cdot L = 4.7548427 \approx 4.75 \end{aligned} \]
The minimal costs can be obtained by substituting the optimal factor combination in the objective function: \[ \begin{aligned} C(K, L) & = 13 K + 13 L\\ & = 61.812955 + 123.62591 \\ & = 185.438865 \approx 185.44 \end{aligned} \]
Given the target output, the minimal costs are \(185.44\).
A firm has the following production function: \[ F(K,L)= K L^{2}. \] The price for one unit of capital is \(p_K = 22\) and the price for one unit of labor is \(p_L = 8\). Minimize the costs of the firm considering its production function and given a target production output of 730 units.
What is the amount of the input factor capital in this minimum?
Step 1: Formulating the minimization problem. \[ \begin{aligned} \min_{K,L} C(K,L) & = p_K K + p_L L\\ & = 22 K + 8 L\\ \mbox{subject~to:} & F(K,L) = Q \\ & K L^{2} = 730 \end{aligned} \] Step 2: Lagrange function. \[ \begin{aligned} \mathcal{L}(K, L, \lambda) & = C(K, L) - \lambda (F(K, L) - Q) \\ & = 22 K + 8 L - \lambda (K L^{2} -730) \end{aligned} \] Step 3: First order conditions. \[ \begin{aligned} \frac{\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial K} & = 22 - \lambda L^{2} = 0\\ \frac{\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial L} & = 8 - {2} \lambda K L^{2 - 1} = 0 \\ \frac{\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial \lambda} & = -(K L^{2}-730) = 0 \end{aligned} \] Step 4: Solve the system of equations for \(K\), \(L\), and \(\lambda\).
Solving the first two equations for \(\lambda\) and equating them gives: \[ \begin{aligned} \frac{22}{L^{2}} & = \frac{8}{2 K L^{2 - 1}}\\ K & = \frac{8}{2 \cdot 22} \cdot L^{2 - (2 - 1)}\\ K & = \frac{8}{44} \cdot L \end{aligned} \] Substituting this in the optimization constraint gives: \[ \begin{aligned} K L^{2} & = 730\\ \left(\frac{8}{44}\cdot L \right) L^{2} & = 730\\ \frac{8}{44} L^{3} & = 730\\ L & = \left(\frac{44}{8} \cdot 730\right)^{\frac{1}{3}} = 15.8938283 \approx 15.89\\ K & = \frac{8}{44} \cdot L = 2.889787 \approx 2.89 \end{aligned} \] Given the target output, the optimal amount of the input factor capital is \(K = 2.89\).
A firm has the following production function: \[ F(K,L)= K L^{}. \] The price for one unit of capital is \(p_K = 10\) and the price for one unit of labor is \(p_L = 24\). Minimize the costs of the firm considering its production function and given a target production output of 720 units.
What is the amount of the input factor labor in this minimum?
Step 1: Formulating the minimization problem. \[ \begin{aligned} \min_{K,L} C(K,L) & = p_K K + p_L L\\ & = 10 K + 24 L\\ \mbox{subject~to:} & F(K,L) = Q \\ & K L^{} = 720 \end{aligned} \] Step 2: Lagrange function. \[ \begin{aligned} \mathcal{L}(K, L, \lambda) & = C(K, L) - \lambda (F(K, L) - Q) \\ & = 10 K + 24 L - \lambda (K L^{} -720) \end{aligned} \] Step 3: First order conditions. \[ \begin{aligned} \frac{\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial K} & = 10 - \lambda L^{} = 0\\ \frac{\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial L} & = 24 - {1} \lambda K L^{1 - 1} = 0 \\ \frac{\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial \lambda} & = -(K L^{}-720) = 0 \end{aligned} \] Step 4: Solve the system of equations for \(K\), \(L\), and \(\lambda\).
Solving the first two equations for \(\lambda\) and equating them gives: \[ \begin{aligned} \frac{10}{L^{}} & = \frac{24}{1 K L^{1 - 1}}\\ K & = \frac{24}{1 \cdot 10} \cdot L^{1 - (1 - 1)}\\ K & = \frac{24}{10} \cdot L \end{aligned} \] Substituting this in the optimization constraint gives: \[ \begin{aligned} K L^{} & = 720\\ \left(\frac{24}{10}\cdot L \right) L^{} & = 720\\ \frac{24}{10} L^{2} & = 720\\ L & = \left(\frac{10}{24} \cdot 720\right)^{\frac{1}{2}} = 17.3205081 \approx 17.32\\ K & = \frac{24}{10} \cdot L = 41.5692194 \approx 41.57 \end{aligned} \] Given the target output, the optimal amount of the input factor labor is \(L = 17.32\).
num exercises have only a single numeric solution (and to make test takers read the exercise carefully), one of three natural quantities in the optimum is selected randomly as the question: the first argument (capital), the second argument (labor), or the minimal function value (costs). The optimal solution is also displayed graphically using a contour plot.(Note that the HTML output contains mathematical equations in MathML, rendered by MathJax using ‘mathjax = TRUE’. Instead it is also possible to use ‘converter = “pandoc-mathjax”’ so that LaTeX equations are rendered by MathJax directly.)
Demo code:
library("exams")
set.seed(403)
exams2html("lagrange.Rmd", mathjax = TRUE)
set.seed(403)
exams2pdf("lagrange.Rmd")
set.seed(403)
exams2html("lagrange.Rnw", mathjax = TRUE)
set.seed(403)
exams2pdf("lagrange.Rnw")